Juniper Research found that businesses in eCommerce, airline ticketing, money transfer, and banking services, will cumulatively lose over
$200 billion to online payment fraud between 2020 and 2024, driven by the increased sophistication of fraud attempts and the rising number of fraud types.
In research published this week, Juniper advises that the payments industry is in the midst of a revolution. They believe that the era of the digital payment is firmly ensconced in our lives and their analysis forecasts that nearly half the world will be using digital wallets by 2024, with transaction values to increase by almost 60% to over $9 trillion in 2024.

The increase in digital services is increasing engagement and offering customers more choices than ever, but it is also driving a rash of new fraud schemes and scams that threaten the infrastructure as well.
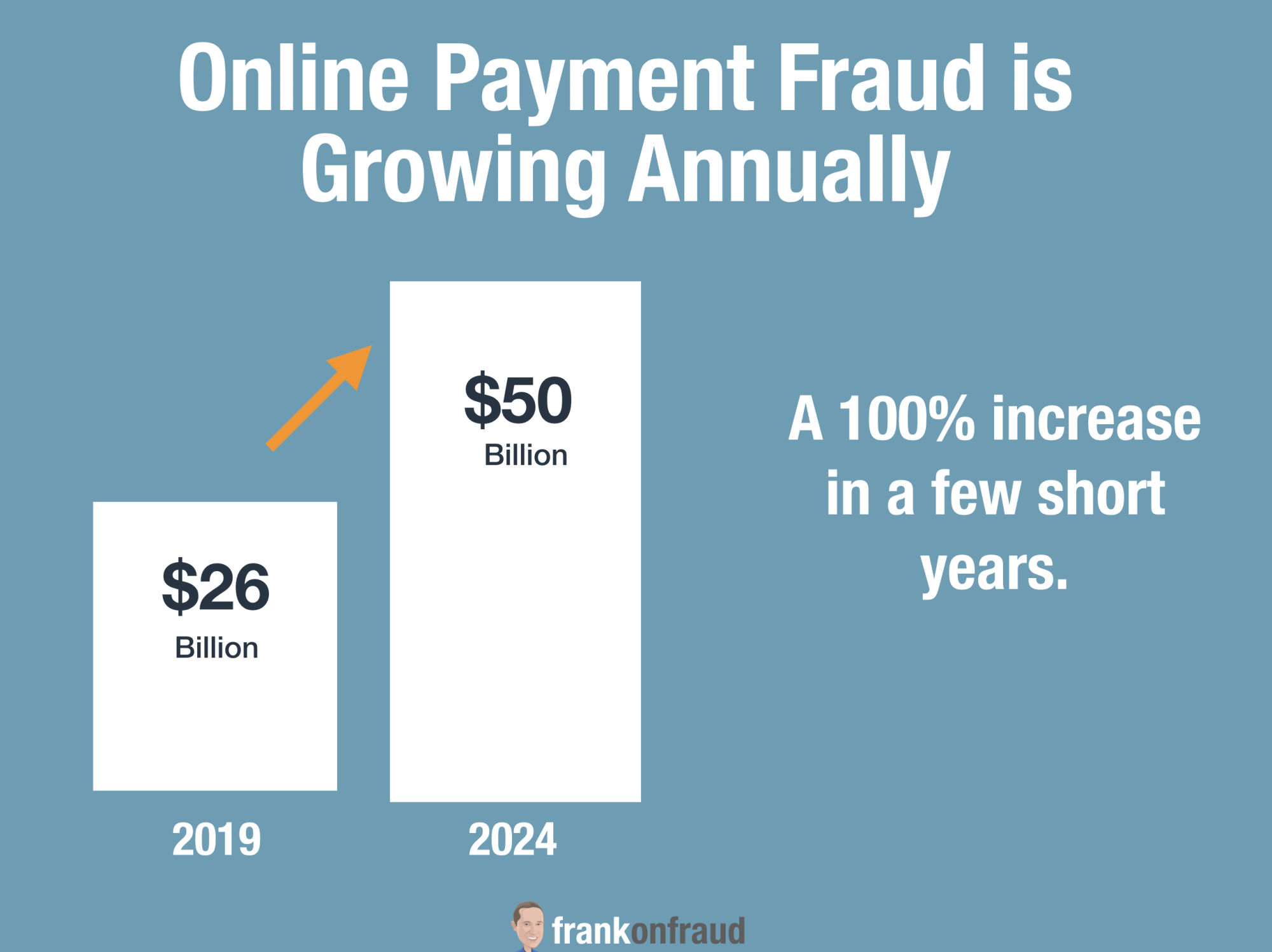
Online Fraud Has Doubled Since 2019
In 2018, Juniper estimated Online Payment fraud was $26 Billion a year. They now estimate it is close to $50 Billion a year.
That is a doubling of Online Fraud is being driven by more sophisticated fraudsters, new products, and more data breach activity.
Online Fraud Will Cause $50 Billion in Losses a Year Due to 11 Fraud Types
Juniper Research shows that new methods of fraud are entering the landscape to reflect new technologies and the fraudsters’ toolkit has become more sophisticated.
They believe that online payment fraud will be driven by 11 different types of fraud.

- Clean Fraud – is a transaction that passes a merchant’s typical checks and appears to be legitimate, yet is actually fraudulent.
- Account Takeover – is a type of identity fraud where criminals attempt to gain access to a consumer’s funds by adding their information to the account.
- Friendly fraud – occurs when a merchant receives a chargeback because the cardholder denies making the purchase or receiving the order.
- Chargeback Fraud – similar to friendly fraud, as a chargeback request is made in spite of received goods and services.
- Identity Fraud – is the fraudulent acquisition and use of sensitive personal information, such as national identification numbers (eg social security numbers), passports and drivers’ licenses.
- Affiliate Fraud – this type of fraud involves the fraudulent use of a company’s lead or referral programs to make a profit.
- Re-shipping – this typically involves fraudsters recruiting an innocent person (known as a ‘mule’) to package and re-ship merchandise purchased with stolen credit cards.
- Botnets – a botnet is a network of infected machines controlled by a fraudster (the ‘botmaster’) to perpetuate a host of crimes. In the case of eCommerce, the infected device could be used with stolen payment and identity information, so the transaction appears to originate from a location that reasonably matches the credit card in use.
- Phishing – is the practice of sending seemingly official emails from legitimate businesses to steal sensitive personal information from customers, such as account login details, passwords, and account numbers.
- Whaling – is a variation of phishing, but targets or ‘spears’ a specific subset of consumers, customers or employees.
- Pharming – re-directs website traffic to an illegal site where customers unknowingly enter their personal data.
- Triangulation – this enables fraudsters to steal credit card information from valid customers, typically through online auctions, ticketing sites, or online classified ads.
Juniper recommends an omnichannel approach and rigorous attention to cybersecurity at every touchpoint and access point in the process.
Spending on Machine Learning Will Grow to $10 Billion Annually by 2024
Machine learning is the primary way that most online payment companies are controlling losses. Juniper believes that the incorporation of machine learning into fraud detection and prevention software will drive spending forward, reaching $10 billion in 2024, a 15% increase on 2020.
Great stuff from Juniper as always.



